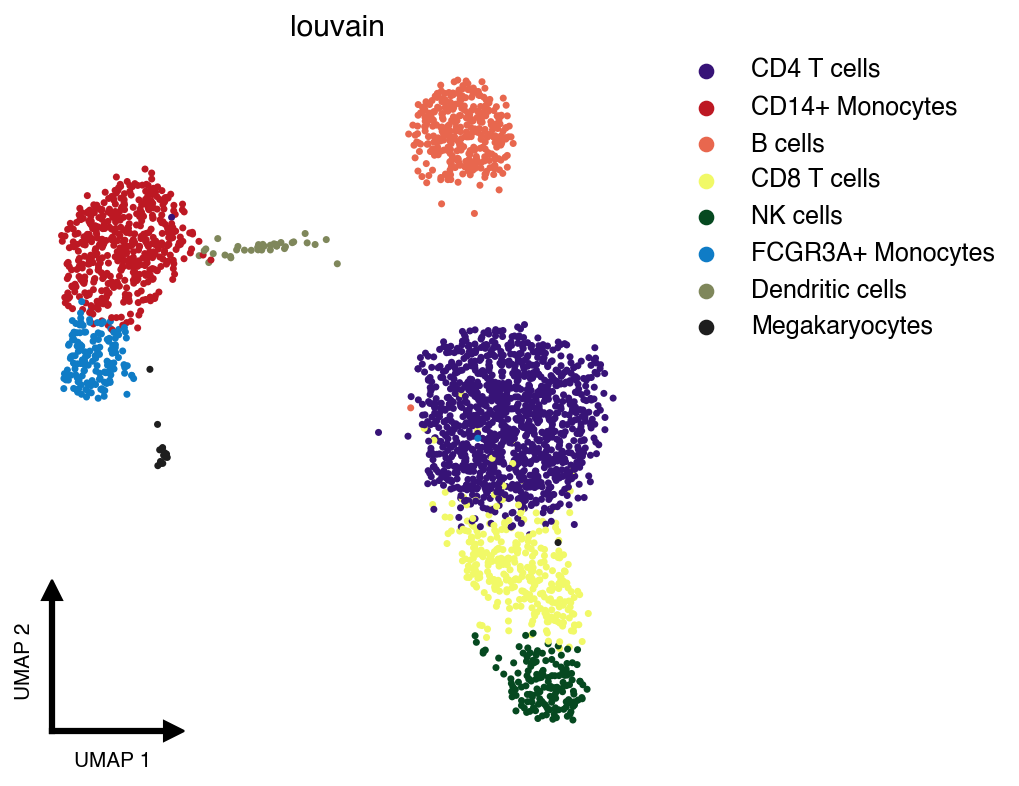A pythonic port of the BuenColors R package for convenient scientific color palettes and matplotlib styles.
Color palettes are a direct port from the R package, with many based on the wesanderson R package.
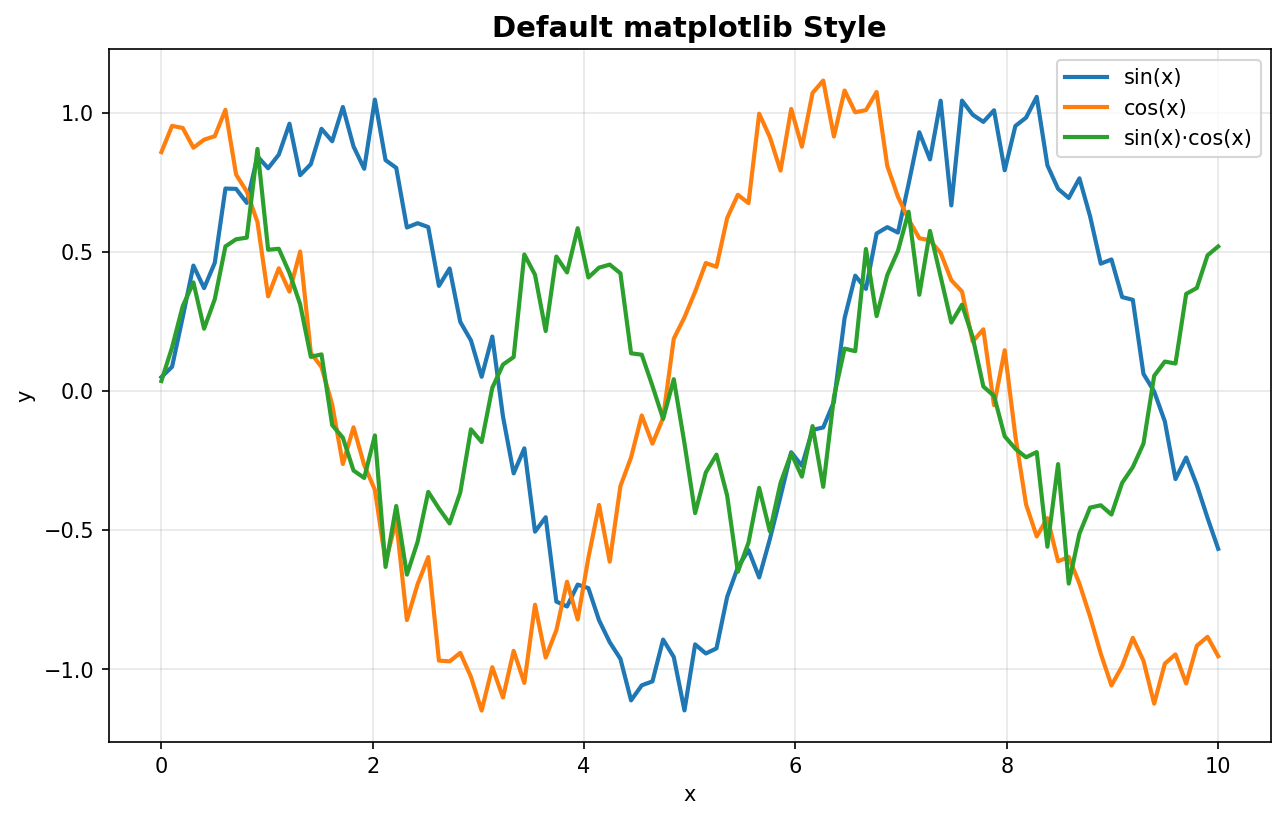
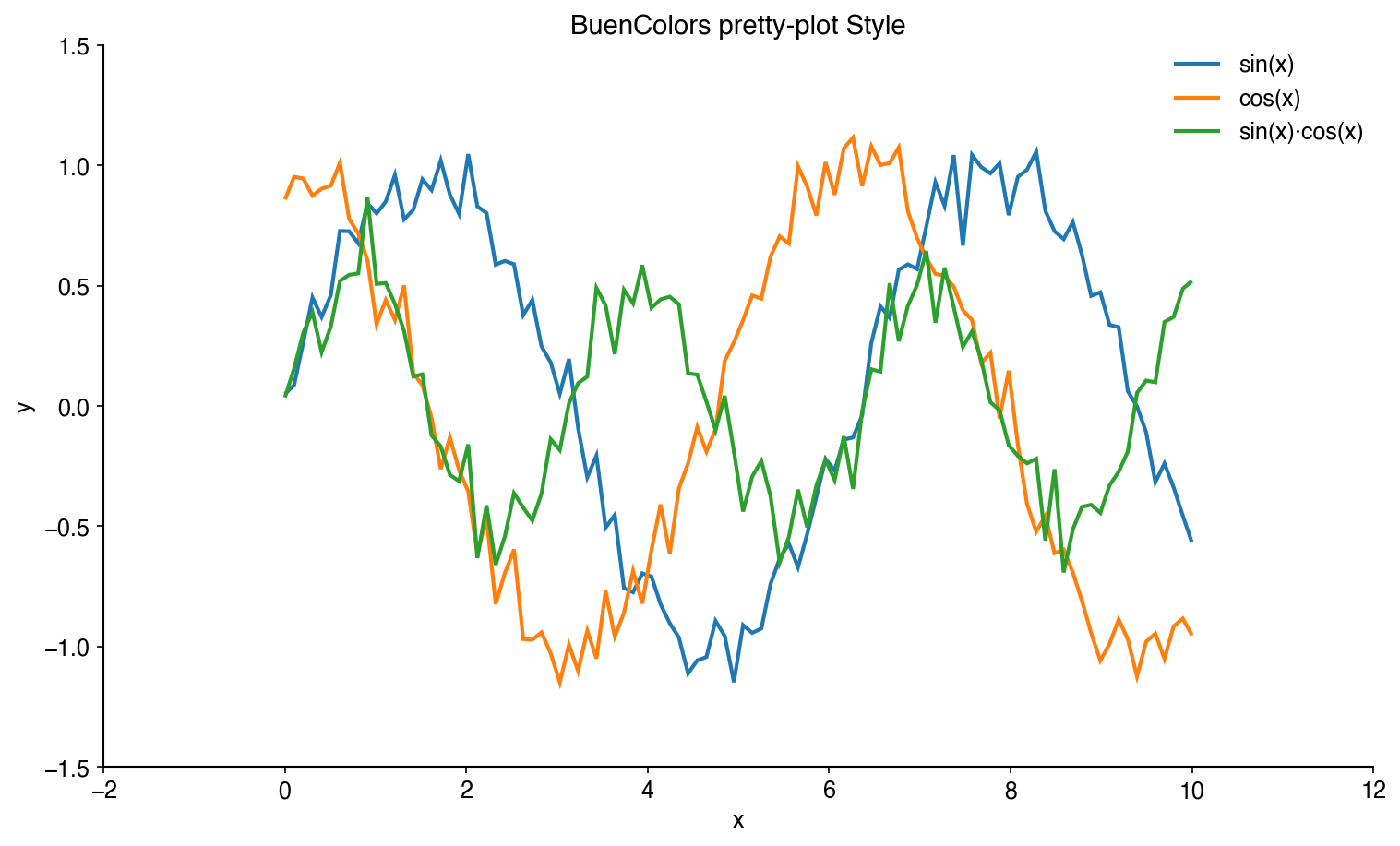
pip install buencolorsThe easiest way to improve your matplotlib plots is to use the included pretty-plot style:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Apply the pretty-plot style
plt.style.use('pretty-plot')
# Create a beautiful plot
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x), label='sin(x)')
plt.plot(x, np.cos(x), label='cos(x)')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.show()Before (default):
After (pretty-plot):
BuenColors automatically registers all palettes as matplotlib colormaps:
import buencolors as bc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# List available palettes
bc.list_palettes()
# Palettes are available directly as colormaps
plt.style.use('pretty-plot')
data = np.random.randn(100, 100)
plt.imshow(data, cmap='Zissou')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
# Or use get_palette() to extract individual colors
colors = bc.get_palette('Zissou')
for i, color in enumerate(colors):
plt.plot([0, 1], [i, i], color=color, linewidth=10)
plt.show()BuenColors provides several utility functions to make your plots publication-ready:
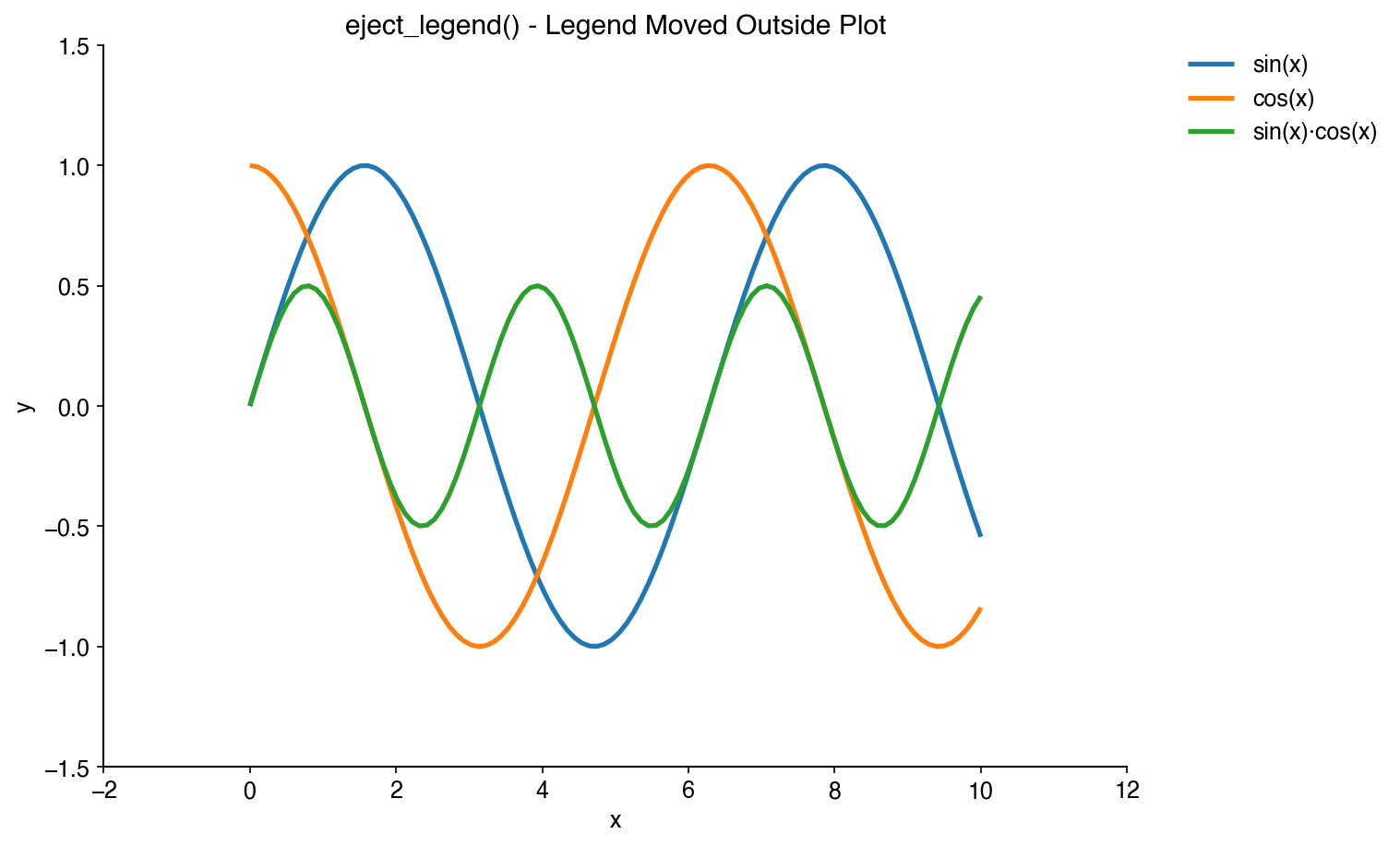
Move legends outside the plot area to avoid obscuring data:
import matplotlib as plt
import buencolors as bc
# Your plot code here
plt.plot(x, y1, label='Dataset 1')
plt.plot(x, y2, label='Dataset 2')
# Eject the legend to the right
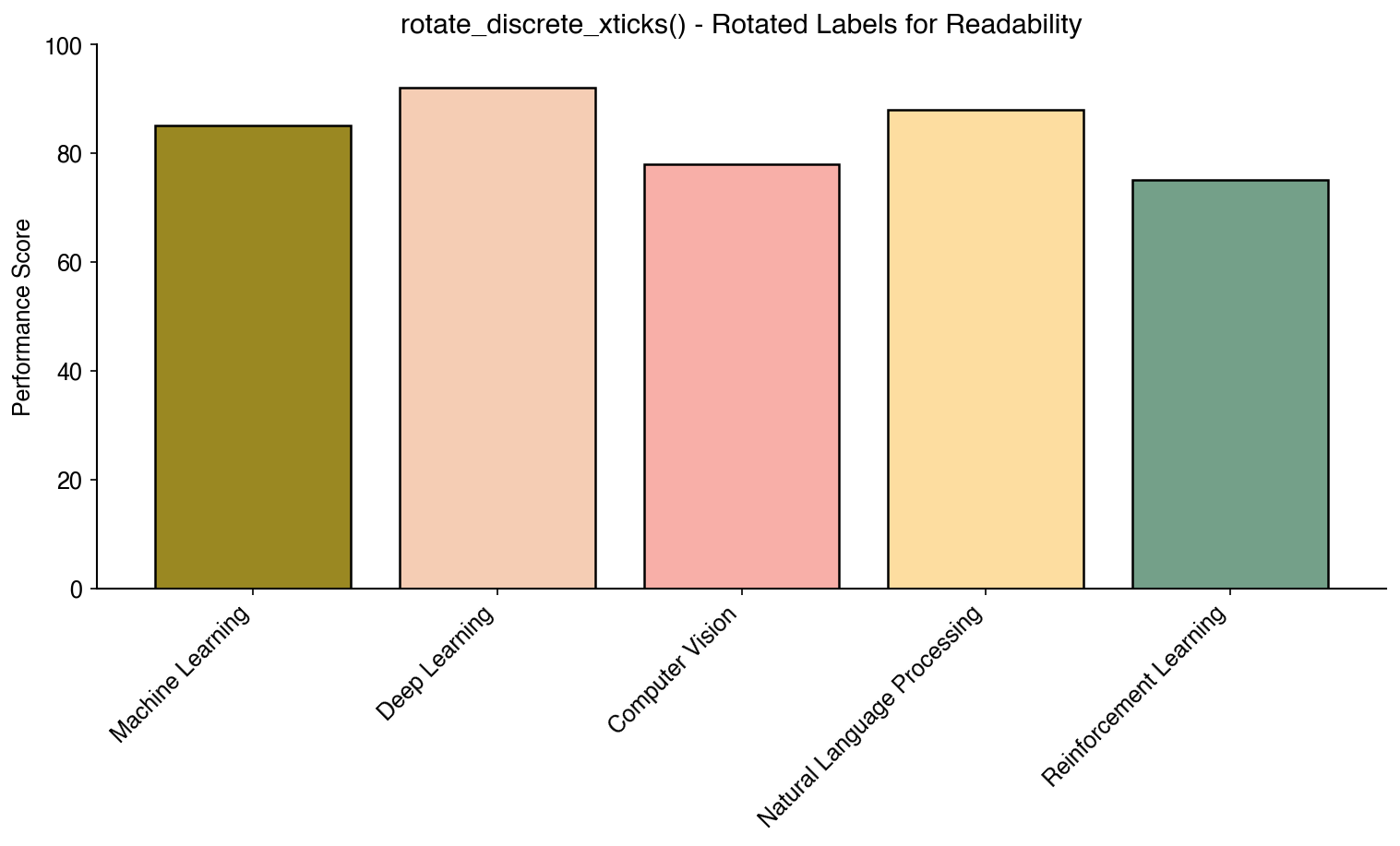
bc.eject_legend()Automatically rotate discrete x-tick labels for better readability:
bc.rotate_discrete_xticks()Extract a legend to a separate figure for independent saving or publication:
# Create a plot with legend
plt.plot(x, y1, label='Dataset 1')
plt.plot(x, y2, label='Dataset 2')
plt.legend()
# Extract legend to separate figure (removes from original by default)
legend_fig = bc.grab_legend()
legend_fig.savefig('legend.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.savefig('plot.pdf') # Plot saved without legend
# Or keep legend on original plot
legend_fig = bc.grab_legend(remove=False)
legend_fig.savefig('legend_copy.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')
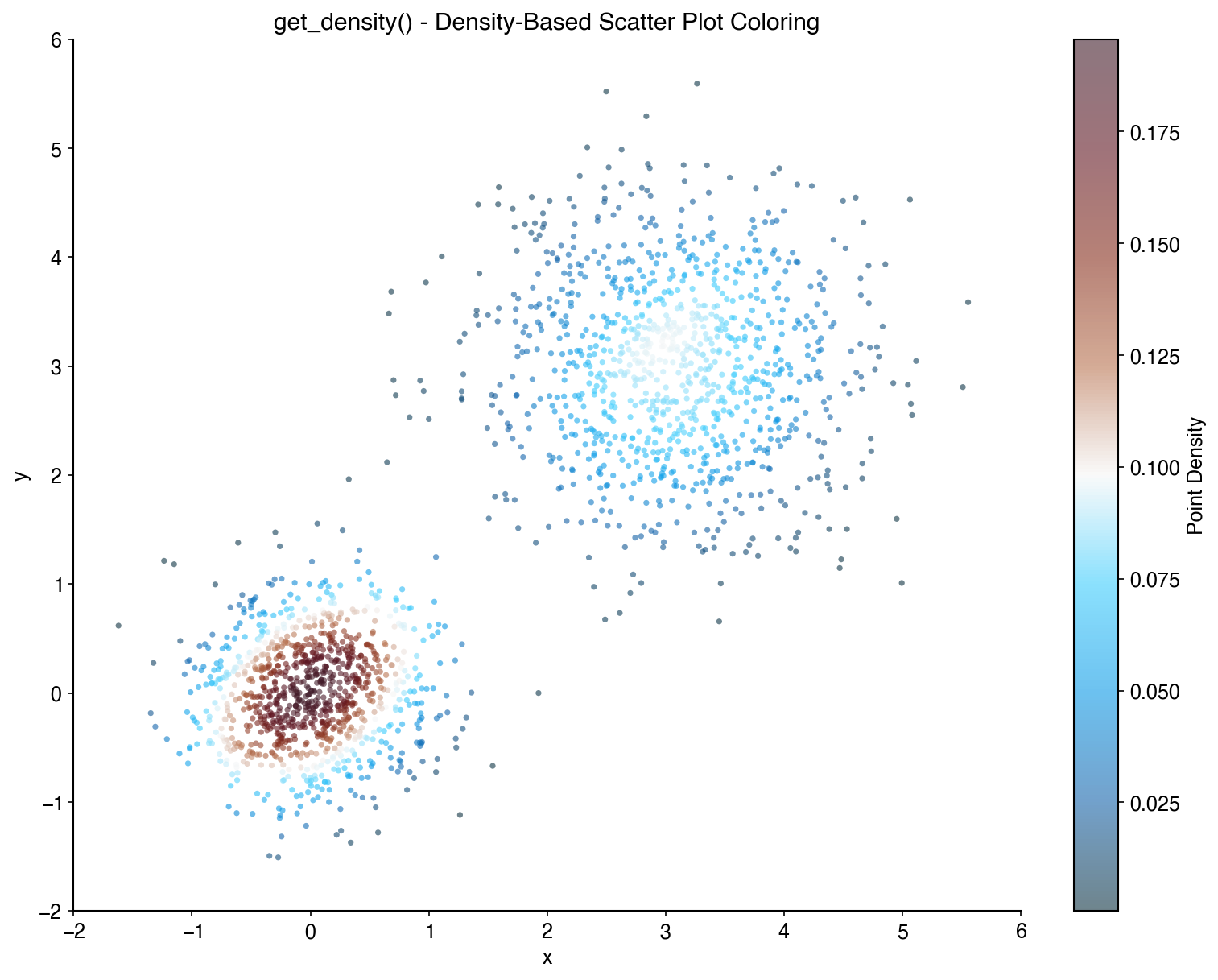
plt.show() # Original plot still has legendColor scatter plot points by their density:
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
density = bc.get_density(x, y)
plt.scatter(x, y, c=density, cmap='viridis', s=5)
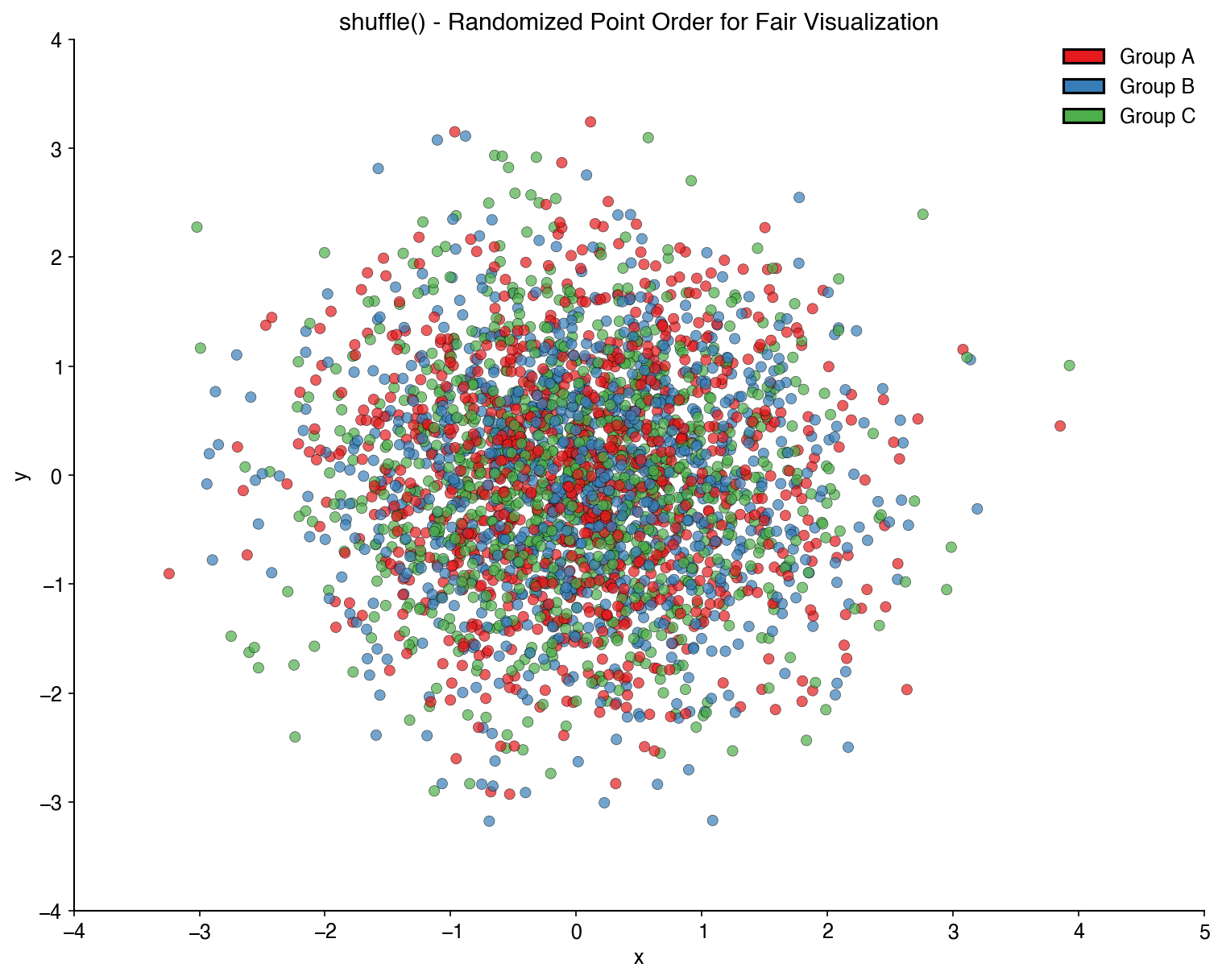
plt.colorbar(label='Density')Randomize the order of plot elements to avoid overplotting bias:
x_shuffled, y_shuffled, colors_shuffled = bc.shuffle(x, y, colors)
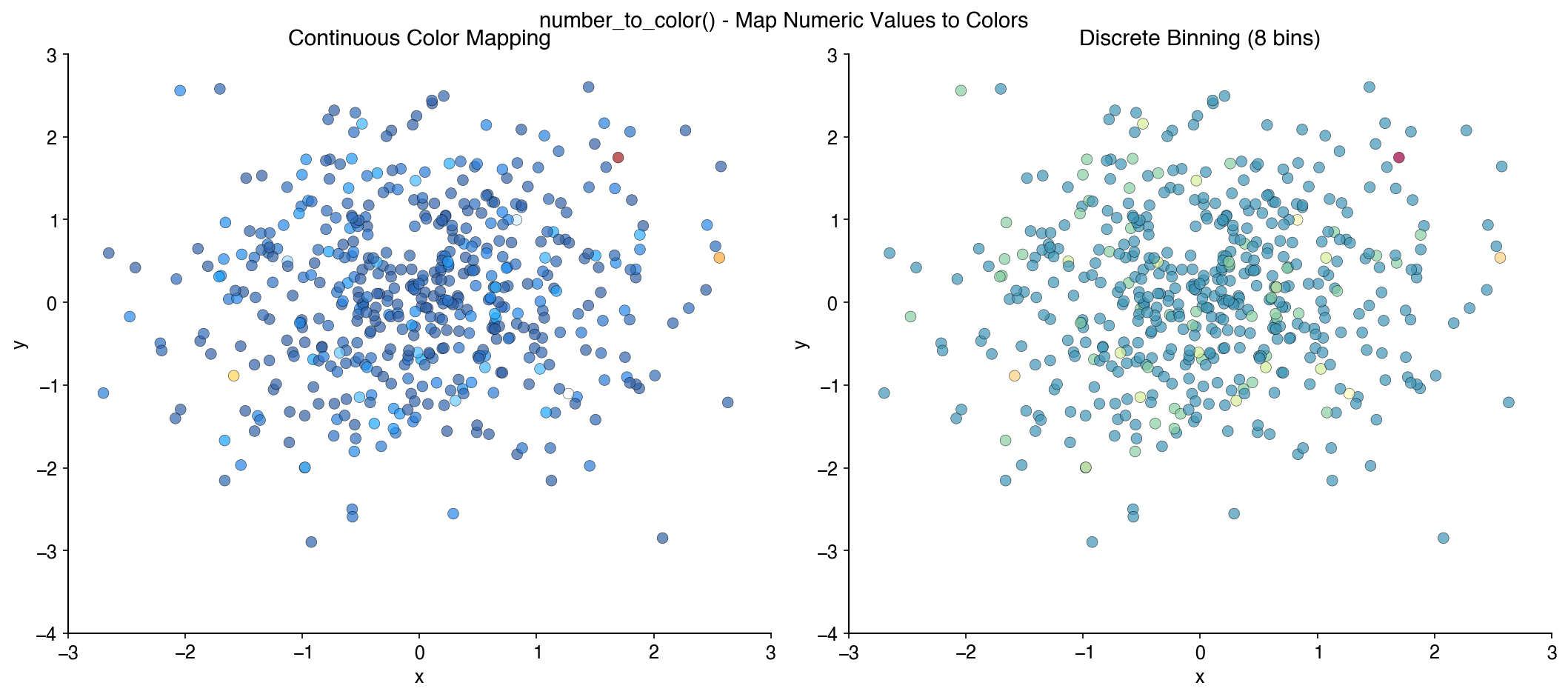
plt.scatter(x_shuffled, y_shuffled, c=colors_shuffled)Map numerical values to colors from a palette:
values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
colors = bc.number_to_color(values, palette='Zissou')BuenColors provides specialized functions for single-cell analysis visualization, designed to work seamlessly with Scanpy and AnnData objects.
To use the single-cell features, install with scanpy and anndata:
pip install buencolors scanpy anndataThe clean_umap() function creates publication-ready UMAP plots with minimal decorations:
import scanpy as sc
import buencolors as bc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load example dataset
adata = sc.datasets.pbmc3k_processed()
# Create a clean UMAP colored by cell type
with plt.style.context('pretty-plot'):
bc.clean_umap(adata, color='louvain', palette='lawhoops')Features of clean_umap():
-
Minimal decorations: No borders, ticks, or frame
-
Custom L-shaped axis indicators: Small arrows showing UMAP dimensions
-
Auto-ejected legend: Automatically positioned to the right to avoid obscuring data
-
Shuffled cells: Randomizes plotting order to avoid non-random ordering artifacts
For detailed examples and interactive notebooks, see the documentation or the docs/examples directory.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
- Original BuenColors R package
- Wes Anderson palettes inspired by wesanderson